Scientific societies have gone in a few months from warning about vitamin D deficiency in the population to warning about the abuse and indiscriminate use of supplements that are offered to correct the deficit. Driven by the covid, these products, which are advertised in stores and on internet pages as an immune system booster, have become a world market of 1.1 billion dollars and are expected to grow at a rate of 7%, reaching the 1.6 billion dollars in 2025, according to Bussines Wire’s prediction. But all medical associations warn of the dangers of indiscriminate use, of the absence of tests that require massive screening of vitamin D levels, of the lack of a universal indicator of adequate concentrations, and of the risk of self-medication.
The demand for tests to find out vitamin D levels has led the United States Preventive Services Task Force to publish a statement in Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) in which they conclude: “There is no general evidence on the benefits of vitamin D deficiency screening. Therefore, the balance between the benefits and harms of vitamin D deficiency screening in asymptomatic adults cannot be determined. ”.
The specialist in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology and Nutrition José Manuel Quesada Gómez, linked to the University of Córdoba, affirms that this resolution is added to the one that all scientific societies have published: “Mass screening is not justified, except in people with symptoms or with obvious risks ”.
The North American team supports this statement: “Vitamin D requirements can vary by individual, so there is no single level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration. [el indicador en sangre más común], which defines the deficiency, and there is no consensus regarding the precise serum levels of vitamin D that represent optimal health or sufficiency ”.
Consuming too much of any nutrient, even one as neutral as water, can have harmful consequences
José Manuel Quesada Gómez, specialist in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology and Nutrition
Quesada Gómez, who from the beginning of his career investigated the methods to measure the concentration of vitamin D in the blood, reaffirms this conclusion. “In general, the minimum levels established in different clinical practice guidelines are above 20 and 30 nanograms per milliliter [ng/mL]. For the healthy population, the European Food Safety Authority considers sufficient levels above 20 ng / mL, while the Spanish Society of Endocrinology and Nutrition considers that they should be above 30 ng / mL. The European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases recommends levels above 20 ng / mL for postmenopausal women and above 30 ng / mL for frail elderly. For its part, the Spanish Society of Rheumatology recommends maintaining 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels above 30 ng / mL for the population with osteoporosis ”.
In any case, both the endocrinologist and medical societies warn that the determination of adequate levels and the prescription of supplements or treatments have to be determined by specialists because, as Quesada Gómez emphasizes, “the excessive consumption of any nutrient, even of one as neutral as water can have harmful consequences ”.
Adverse effects
The US National Institutes of Health (NIH) confirm it: “Consuming too much vitamin D can be harmful. Too high concentrations in the blood (greater than 150 ng / mL) can cause nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, confusion, pain, loss of appetite, dehydration, excessive urination and thirst, kidney stones, kidney failure, arrhythmia and even death. ”.
These adverse effects have a main origin, according to the NIH: “High levels of vitamin D are almost always due to its consumption in excessive amounts through dietary supplements.”
Excessively high concentrations of vitamin D in the blood are almost always due to its consumption in excessive amounts through dietary supplements and can range from kidney failure and arrhythmia to death
US National Institutes of Health (NIH)
The assimilation of the so-called vitamin D, since it is a hormone, is produced by cutaneous synthesis thanks to solar radiation (80%) and diet (20%). These sources may not be sufficient in certain cases for populations that live in areas with little insolation or that present risk factors. But only a specialist can determine it and it cannot be corrected with self-consumption of supplements. Quesada Gómez, who has been president of the Spanish Society for Bone Research and Mineral Metabolism, simplifies it with an illustrative example to explain the reason: “Not everything that reaches the liver is transformed into calcifediol, the substrate, the raw material that generates vitamin D. It is like a Japanese man with a pocket full of yen in Madrid: if he does not change them, he will not be able to drink a pint ”.
Vitamin D and covid
Despite all the warnings, which led to the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products to post a note for avoid severe cases of hypercalcaemia in pediatrics and in adult patients due to overdose, the consumption of supplements continues to grow and the reason is covid. Vitamin D strengthens the immune system, so a simple, but wrong, deduction has been the trigger: the greater the consumption of products that include it, the greater the body’s defense capacity against the coronavirus.
But it’s not that simple. The generation of vitamin D requires prior biotransformation and this is achieved by a prohormone that acts as a precursor to reach the necessary levels that contribute to a better response to covid. It is calcifediol, which is produced in the liver by a chemical reaction (hydroxylation of vitamin D3) thanks to an enzyme, an organic molecule that acts as a catalyst.
Luis Manuel Training, pulmonologist at the Reina Sofía Hospital in Córdoba and co-author of an investigation by the Maimonides Institute for Biomedical Research in Córdoba on the effects of calcifediol against covid, warns that it must be administered by medical prescription after knowing the existing levels in the body to supply the proper amount and avoid adverse effects.
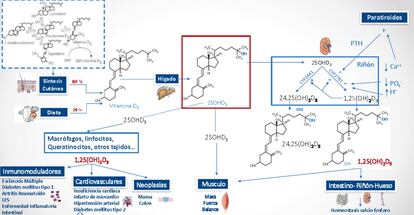
According to Training, calcifediol “acts as an immunomodulator” (stimulator of the body’s immune system to defend itself against viruses), “improves capillary alveolus permeability” (facilitating gas exchange) and “reduces blood coagulability” and, therefore Therefore, the risks of thrombosis.
In the pilot, randomized and open study out of 76 patients, 50 received calcifediol and only one required admission to the Intensive Care Unit. Half of the other 26 received placebo and went through ICU. The best response of calcifediol to covid occurs in blood concentrations of about 50 nanograms per milliliter (ng / mL), according to Quesada Gómez.
“The fascination with vitamin D supplementation began with the discovery in the early 1920s that it prevented rickets. It was driven by the recognition of other potential benefits, including immune function, cardiovascular health and cancer, “he recalls. The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology. However, the same publication warns that, while the data on the role of vitamin D in bone growth and maintenance are clear, the evidence supporting its role in other health processes and diseases, particularly in acute infection of the bones. airway, remains irregular.
José Manuel Quesada Gómez recalls that the recommendation is “to perform 25OHD measurements, in addition to osteoporotic patients with a history or not of non-traumatic fractures (particularly before starting treatment with osteoactive, anticatabolic or anabolic agents), in elderly people with a history of falls, pregnant and lactating women, obese (children and adults), people with insufficient sun exposure, patients with malabsorption syndromes (congenital or acquired), chronic kidney disease or liver failure, cystic fibrosis, hyperparathyroidism, among others.
You can follow MATTER on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram, or sign up here to receive our weekly newsletter.
#vitamin #pandemic
source https://pledgetimes.com/the-vitamin-d-pandemic/
Disqus comments